Have you ever wondered how your body responds to stress? It’s fascinating how our bodies are equipped with systems that kick in during stressful moments. A key player in this response is the adrenal glands. These small but mighty glands sit atop your kidneys, and understanding their role can help you grasp how your body handles stress.
What Are the Adrenal Glands?
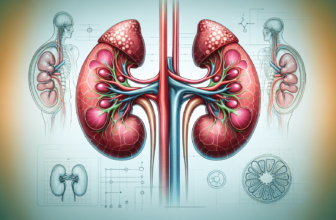
The adrenal glands are two small, triangular-shaped glands located on top of each kidney. They are essential for various bodily functions, including the stress response. Each gland consists of two parts: the adrenal cortex and the adrenal medulla. The cortex produces hormones such as cortisol and aldosterone, while the medulla produces adrenaline and noradrenaline. Each of these hormones plays a vital role in how you respond to stress.
The Structure of the Adrenal Glands
To help you visualize the adrenal glands, think of them as two small hats on top of kidneys.
| Part of the Adrenal Gland | Function |
|---|---|
| Adrenal Cortex | Produces hormones that regulate metabolism, immune response, and blood pressure. |
| Adrenal Medulla | Produces adrenaline and noradrenaline, important for fight-or-flight response. |
Understanding this structure gives you insight into how different parts of the glands contribute to your body’s reaction to stress.
The Stress Response
When you encounter a stressful situation, whether it’s a looming deadline or a sudden scare, your body goes into an automatic mode of defense. This is known as the stress response, or the “fight-or-flight” response, which involves a complex series of hormonal and physiological changes that prepare you to either face the threat or escape from it.
How Stress Triggers Hormonal Release
When faced with stress, your brain signals the hypothalamus, which in turn activates the pituitary gland. This gland sends a message to the adrenal glands, instructing them to release certain hormones into your bloodstream. Here’s how it unfolds:
- Hypothalamus Activation: Your brain detects stress and triggers the hypothalamus.
- Pituitary Gland Response: The hypothalamus sends signals to the pituitary gland.
- Adrenal Activation: The pituitary gland releases adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH), which stimulates the adrenal glands to release cortisol and adrenaline.
This entire process is known as the HPA (hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal) axis.
The Role of Cortisol
Cortisol, known as the “stress hormone,” has several essential roles during stress responses:
- Increases Blood Sugar Levels: Cortisol helps to provide your body with the energy it needs to respond to stress by increasing glucose availability.
- Suppresses the Immune System: While this might sound negative, it’s a crucial part of the body’s immediate survival strategy, preventing inflammation during a short-term stress response.
- Regulates Metabolism: Cortisol plays a role in how your body processes nutrients and manages energy levels.
The Role of Adrenaline and Noradrenaline
Adrenaline (epinephrine) and noradrenaline (norepinephrine) are critical during a stress response. These hormones instigate immediate physical changes, including:
- Increased Heart Rate: Your heart pumps faster to deliver more oxygen to your muscles.
- Elevated Blood Pressure: This helps circulate blood more efficiently throughout your body.
- Dilation of Airways: More air enters your lungs to improve oxygen intake.
- Increased Alertness: Your body becomes more alert, enhancing your ability to respond quickly.
Chronic Stress and the Adrenal Glands
While short bursts of stress can be manageable and even motivating, chronic stress can wreak havoc on your adrenal glands and the hormones they produce. Over time, your body may become exhausted from prolonged exposure to stress hormones, leading to a condition known as adrenal fatigue.
What is Adrenal Fatigue?
Adrenal fatigue is a theoretical condition that may occur when the adrenal glands are overworked due to chronic stress. Although it is not universally recognized as a medical diagnosis, the symptoms can be very real for those experiencing them.
Some common signs of adrenal fatigue may include:
- Fatigue: Persistent exhaustion that doesn’t improve with rest.
- Poor Stress Management: Difficulty managing stress or an increased sensitivity to stress.
- Sleep Disturbances: Trouble sleeping or feelings of sleepiness during the day.
- Cravings: Increased cravings for salty or sweet foods.
The Impact of Chronic Stress on Health
Chronic stress can lead to various physical and mental health issues.
| Physical Effects | Mental Health Effects |
|---|---|
| Weakened Immune System | Anxiety |
| Weight Gain or Loss | Depression |
| Digestive Issues | Mood Swings |
| Cardiovascular Problems | Irritability |
Understanding how chronic stress impacts health emphasizes the importance of managing stress effectively.
Ways to Support Your Adrenal Glands
Taking care of your adrenal glands can improve your overall well-being and help you manage stress effectively. Here are a few strategies:
1. Eat a Balanced Diet
A well-rounded diet can support hormone production and overall health. Focus on:
- Whole Foods: Incorporate fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins.
- Healthy Fats: Examples include avocados, nuts, and olive oil.
- Hydration: Drink plenty of water to support bodily functions.
2. Manage Stress Through Mindfulness
Practicing mindfulness techniques, such as meditation or deep-breathing exercises, can help you manage stress more effectively.
- Meditation: Spend a few minutes daily focusing on your breath and being in the present moment.
- Yoga: Engage in gentle yoga practices to calm your mind and reduce stress levels.
3. Incorporate Regular Exercise
Physical activity is essential for overall health and can significantly reduce stress. Aim for at least 30 minutes of moderate exercise most days of the week. Activities can include:
- Walking
- Swimming
- Dancing
- Cycling
4. Prioritize Sleep
Adequate sleep is crucial for hormone regulation and stress management. Aim for 7-9 hours of quality sleep each night.
- Sleep Hygiene: Create a relaxing bedtime routine, and keep your sleeping environment dark and cool.
5. Seek Professional Help
If you’re struggling to manage stress or suspect adrenal fatigue, consulting a healthcare professional can provide support and guidance tailored to your needs.
Conclusion
Understanding the intricate relationship between your adrenal glands and your body’s stress response is crucial for maintaining overall health. These small glands play a significant role in how you handle stress, and supporting their function through healthy lifestyle choices can lead to improved well-being. By paying attention to your body’s signals and managing stress effectively, you can promote resilience and a more balanced life.
So, the next time you find yourself facing a stressful situation, remember the vital role that your adrenal glands play and consider how you can support them. Your body is designed to handle stress, but with the right practices, you can ensure that it does so effectively and healthily.