Have you ever wondered what those little glands sitting atop your kidneys are up to? You might be surprised to find out that the adrenal glands play a crucial role in keeping your body balanced and functioning properly. Let’s unravel the mysteries of the adrenal glands and discover their importance in your overall health.
What Are the Adrenal Glands?
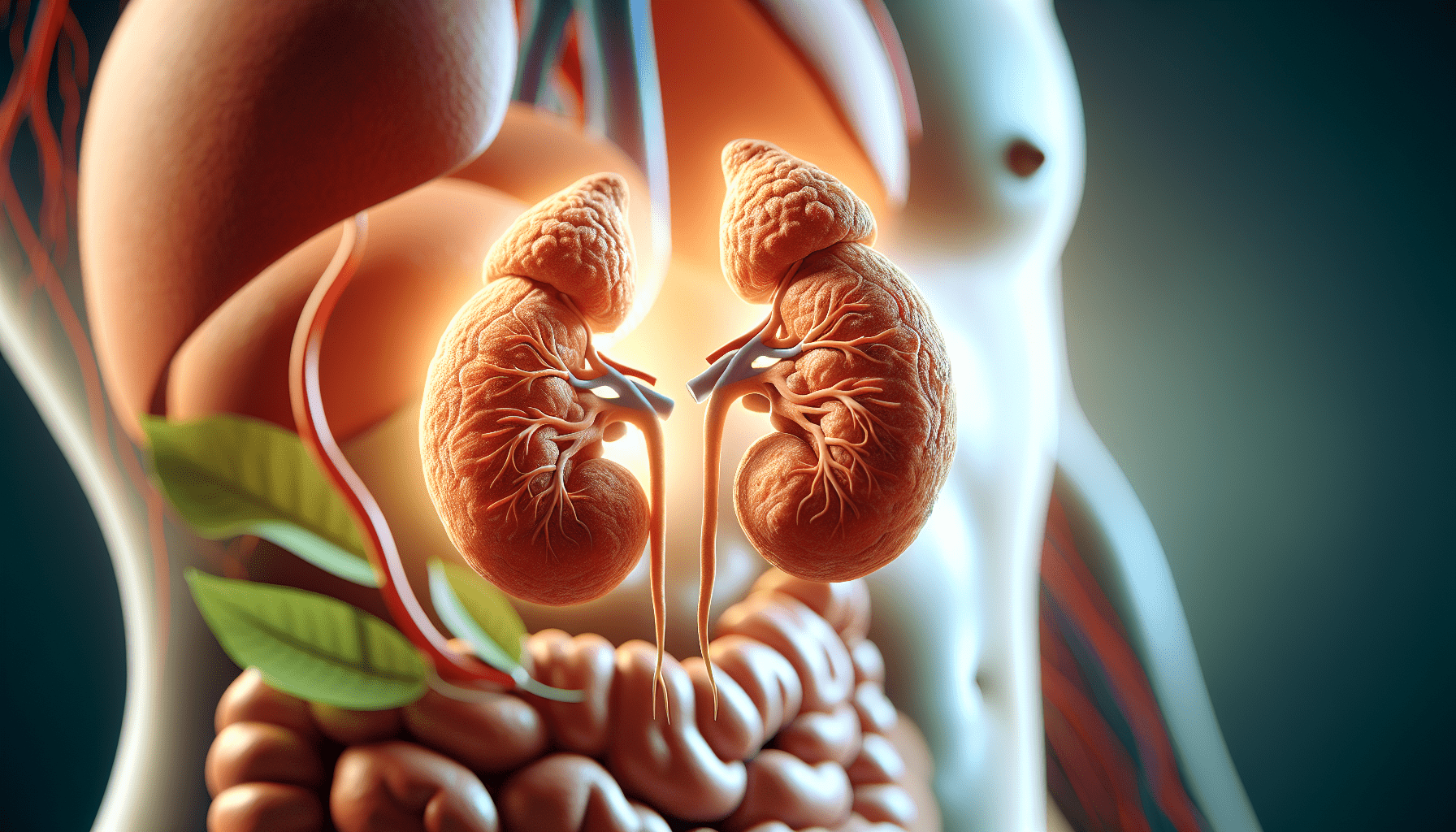
The adrenal glands are small, triangular-shaped glands located on top of each kidney. Despite their tiny size, about 1 to 2 inches long, they are incredibly powerful and responsible for producing a variety of hormones that help regulate numerous functions in your body. Every day, your adrenal glands play a key role in responding to stress, maintaining metabolism, and supporting your immune system, among other functions. Understanding how these glands work can provide you with insights into your health.
The Structure of the Adrenal Glands
Each adrenal gland is composed of two main parts: the adrenal cortex and the adrenal medulla. These two parts work together, but they have different roles and secrete different hormones.
Adrenal Cortex
The adrenal cortex is the outer layer of the adrenal gland. It is responsible for producing three main types of hormones:
- Glucocorticoids: These hormones, including cortisol, help regulate metabolism, reduce inflammation, and control your body’s stress response.
- Mineralocorticoids: Aldosterone, a primary mineralocorticoid, plays a vital role in regulating sodium and potassium levels, which in turn helps control blood pressure.
- Androgens: Although they are often referred to as male hormones, androgens are produced by both men and women and are involved in the development of muscle mass and bone density.
Adrenal Medulla
The adrenal medulla is the inner part of the adrenal gland. It produces catecholamines, including:
- Adrenaline (Epinephrine): This is the hormone that fuels your fight-or-flight response. It increases heart rate, elevates blood pressure, and boosts energy supplies during times of stress or danger.
- Norepinephrine (Noradrenaline): Similar to adrenaline, norepinephrine helps regulate blood pressure and glucose levels while enhancing your body’s response to stress.
Functions of the Adrenal Glands
Now that you have a basic understanding of what the adrenal glands are and their structure, let’s take a closer look at the specific functions they serve in your body.
1. Stress Response
One of the most important functions of the adrenal glands is responding to stress. When you encounter a stressful situation—be it physical, emotional, or psychological—your body releases cortisol and adrenaline. These hormones work together to prepare your body for a quick response. For example, when you feel threatened, adrenaline increases your heart rate and energy, while cortisol helps ensure that your body’s metabolism supports this heightened state of alertness.
2. Metabolism Regulation
The hormones produced by your adrenal glands play a significant role in regulating metabolism. Cortisol, for instance, helps maintain blood sugar levels by facilitating the conversion of fats and proteins into glucose. This regulation is essential for overall energy management and ensures that your body has adequate fuel throughout the day.
3. Immune Function
Cortisol also affects your immune function. While it helps control inflammation and immune response, chronic high levels of cortisol can suppress your immune system, making you more susceptible to infections. It’s a delicate balance that the adrenal glands help manage to keep you healthy.
4. Blood Pressure Regulation
The adrenal glands also have a direct impact on your blood pressure through the secretion of aldosterone. This hormone helps control the balance of sodium and potassium in your body. When your sodium levels are low, aldosterone is secreted to retain sodium, causing water retention, which increases blood volume and consequently raises blood pressure.
5. Electrolyte Balance
In addition to regulating blood pressure, aldosterone helps maintain proper electrolyte balance. This balance is crucial for normal cell function, hydration, and muscle function. Your adrenal glands ensure that your body has the right amounts of sodium, potassium, and other electrolytes needed to function optimally.
Understanding Hormonal Imbalances
Sometimes, your adrenal glands can become overactive or underactive, leading to hormonal imbalances that can affect your health significantly. Understanding these conditions is essential for taking charge of your well-being.
Adrenal Insufficiency
Adrenal insufficiency, also known as Addison’s disease, occurs when the adrenal glands do not produce adequate amounts of cortisol and, in some cases, aldosterone. This condition can lead to fatigue, weight loss, low blood pressure, and changes in skin pigmentation. Most people experience these symptoms slowly over time, which can make diagnosis challenging.
Cushing’s Syndrome
On the other end of the spectrum, Cushing’s syndrome occurs when there are elevated levels of cortisol. This condition can result in symptoms such as rapid weight gain, particularly in the face and upper body, high blood pressure, and changes in mood. Cushing’s syndrome can be caused by various factors, including tumors on the adrenal glands or prolonged use of corticosteroid medications.
Lifestyle Tips for Healthy Adrenal Glands
Supporting your adrenal glands through lifestyle choices can help you maintain their health and function. Here are some friendly suggestions to keep your adrenal glands thriving:
1. Manage Stress
Since adrenal glands are closely linked to your body’s stress response, finding healthy ways to manage stress is crucial. Consider incorporating practices like meditation, yoga, or deep-breathing exercises into your daily routine. Even taking a few moments to relax and unwind can make a big difference.
2. Prioritize Sleep
Quality sleep is essential for the balance of hormones, including those produced by your adrenal glands. Aim for 7-9 hours of sleep per night and establish a relaxing bedtime routine. This can help your body recover and recharge, allowing your adrenal glands to function optimally.
3. Maintain a Balanced Diet
A nutritious diet plays a vital role in supporting adrenal health. Focus on whole foods that are rich in vitamins and minerals. Include plenty of fruits, vegetables, lean proteins, and healthy fats in your meals. Make sure to stay hydrated throughout the day, as proper hydration can influence hormonal balance.
4. Regular Exercise
Moderate exercise can help reduce stress levels and promote hormonal balance. Activities like walking, cycling, and swimming are great ways to get moving without overwhelming your body. Aim for at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity exercise each week to keep your adrenal system in check.
5. Limit Stimulants
Excessive caffeine and sugar can put extra strain on your adrenal glands. While an occasional cup of coffee is fine, consider reducing your intake to maintain steady energy levels throughout the day. Opting for nutritious snacks instead of sugary treats can also help prevent energy crashes that stress your adrenal glands.
When to Seek Help
If you suspect that your adrenal glands may not be functioning properly, such as experiencing chronic fatigue, unexplained weight changes, or other concerning symptoms, it’s important to seek medical advice. A healthcare professional can perform tests to evaluate your adrenal function and help determine the appropriate treatment if necessary.
Conclusion
Understanding what the adrenal glands do can empower you to take charge of your health. These small yet mighty glands play a significant role in your body’s response to stress, metabolism regulation, and maintaining overall balance. By incorporating healthy lifestyle habits and being aware of potential issues, you can support your adrenal health and enhance your well-being. Remember, keeping your adrenal glands in good shape is just one of the many ways you can promote a healthy and vibrant life.