What is the first thing that comes to mind when you think about adrenal insufficiency? It might sound complex, but it’s a condition that affects many people around the world. Let’s unpack what adrenal insufficiency (also known as Addison’s disease) is all about and what it means for those who live with it.
Understanding Adrenal Insufficiency
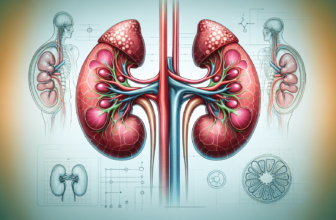
Adrenal insufficiency occurs when your adrenal glands, which are located on top of your kidneys, don’t produce enough of certain hormones. These hormones are critical for many body functions, including metabolism, immune response, and blood pressure regulation. When your body lacks these hormones, it can lead to a variety of symptoms that may affect your daily life.
What Are the Adrenal Glands?
Your adrenal glands are small, triangular-shaped glands that play a significant role in your body’s function. They produce several hormones, including:
| Hormone | Function |
|---|---|
| Cortisol | Helps control blood sugar levels, regulate metabolism, and reduce inflammation. |
| Aldosterone | Regulates sodium and potassium levels, which helps control blood pressure. |
| Adrenaline | Known as the “fight or flight” hormone, it helps your body respond to stress. |
| DHEA | A precursor to sex hormones and involved in the development of male and female characteristics. |
These hormones collectively help manage your body’s response to stress, maintain homeostasis, and regulate various bodily functions.
What Causes Adrenal Insufficiency?
Adrenal insufficiency can stem from several causes, and understanding these can help you grasp the condition better. The primary causes can be categorized into two groups: primary adrenal insufficiency and secondary adrenal insufficiency.
Primary Adrenal Insufficiency (Addison’s Disease)
Addison’s disease is the term commonly used for primary adrenal insufficiency. This condition occurs when the adrenal glands are damaged and unable to produce sufficient amounts of hormones. Some common causes include:
- Autoimmune Disorders: Your immune system mistakenly attacks the adrenal glands, leading to inflammation and hormonal deficiency.
- Infections: Certain infections, like tuberculosis, can damage adrenal glands.
- Cancer: Tumors or metastases (spread of cancer) can affect adrenal function.
Secondary Adrenal Insufficiency
This form of adrenal insufficiency occurs when the pituitary gland, located at the base of your brain, doesn’t produce enough adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH), which stimulates the adrenal glands. Some causes of secondary adrenal insufficiency include:
- Pituitary Disorders: Issues such as tumors or infections affecting the pituitary gland.
- Long-Term Use of Corticosteroids: Your body may stop its own production of hormones if you’ve been taking steroids for an extended period.
Who Is at Risk?
While adrenal insufficiency can affect anyone, certain risk factors can increase your chances of developing the condition:
- Age: It’s most commonly diagnosed in people aged 30 to 50.
- Family History: A family history of autoimmune diseases may increase your risk.
- Other Autoimmune Conditions: If you have other autoimmune disorders (like type 1 diabetes), you may be more prone to developing Addison’s disease.
Recognizing Symptoms
Understanding the symptoms of adrenal insufficiency can help you seek the right treatment. Symptoms can vary widely and may include:
- Chronic Fatigue: Feeling persistently tired can be one of the earliest signs.
- Weight Loss: Unintended weight loss often occurs due to appetite loss and metabolic changes.
- Low Blood Pressure: You might experience dizziness or lightheadedness when standing.
- Skin Changes: You may notice dark patches or increased pigmentation, especially on scars or skin folds.
Other symptoms can include nausea, vomiting, abdominal pain, and muscle weakness. It’s essential to remember that these symptoms may overlap with other health issues.
Diagnosis of Adrenal Insufficiency
If you suspect you might have adrenal insufficiency, consulting a healthcare professional is crucial. They may perform several tests to confirm the diagnosis:
Blood Tests
- Cortisol Level: This test measures the cortisol level in your blood. Low levels are indicative of adrenal insufficiency.
- ACTH Level: A low cortisol level with high ACTH can indicate primary adrenal insufficiency.
Stimulation Tests
- ACTH Stimulation Test: In this test, your doctor will give you a dose of synthetic ACTH and measure your body’s cortisol response. A low response suggests adrenal insufficiency.
Imaging Tests
- CT or MRI Scan: Imaging may be used to check for abnormalities in the adrenal glands or pituitary gland.
Treatment Options
Living with adrenal insufficiency doesn’t mean you have to live in discomfort. Proper treatment and management can help you maintain a healthy lifestyle. Here are common treatment options:
Hormone Replacement Therapy
The primary treatment for adrenal insufficiency is hormone replacement therapy. This usually involves taking glucocorticoids to replace cortisol. Some common medications include:
| Medication | Type |
|---|---|
| Hydrocortisone | Glucocorticoid |
| Prednisone | Glucocorticoid |
| Cortisone | Glucocorticoid |
Your healthcare provider will determine the appropriate dosage and regimen based on your individual needs.
Mineralocorticoid Replacement
In some cases, you may need additional medications to replace aldosterone. Fludrocortisone is a common medication used for this purpose.
Managing Addison’s Disease
Living with Addison’s disease requires a proactive approach to healthcare. Here are some tips for managing the condition effectively:
Regular Monitoring
It’s essential to monitor your symptoms and follow up with your healthcare team regularly. Make a habit of:
- Keeping a record of your symptoms and any changes you notice.
- Attending scheduled appointments with your healthcare provider to ensure optimal treatment.
Stress Management
Since stress can exacerbate symptoms of adrenal insufficiency, finding ways to manage stress is crucial. Consider the following:
- Relaxation Techniques: Practices like yoga, meditation, or deep breathing exercises can help manage stress levels.
- Adequate Rest: Be sure to get enough sleep and incorporate rest periods into your day.
Nutrition
Eating a well-balanced diet can have a significant impact on how you feel. Aim to include:
- Adequate Salt Intake: Your doctor may recommend increasing your salt intake since adrenal insufficiency can affect sodium levels.
- Balanced Meals: Focus on whole foods, including fruits, vegetables, lean proteins, and healthy fats.
Emergency Preparedness
For those with adrenal insufficiency, it’s essential to be prepared for emergencies, especially during times of stress or illness. Here’s what you can do:
- Carry a Medical Card: Keep a card that states you have Addison’s disease and your treatment plan.
- Know Your Signs of Crisis: Recognizing symptoms of an adrenal crisis, such as severe fatigue, confusion, or a sudden drop in blood pressure, is vital.
- Emergency Kit: Consider carrying an emergency injection kit containing hydrocortisone to use if you cannot take medications orally.
Living with Addison’s Disease
While living with Addison’s disease can present challenges, many adults lead full and active lives with proper management. Here are a few strategies to help you thrive:
Support Networks
Connecting with others who have similar experiences can be incredibly beneficial. Look for local or online support groups where you can share insights, tips, and encouragement.
Education
Understanding your condition empowers you to make informed decisions about your health. Seek trustworthy resources and educate yourself about adrenal insufficiency.
Mindfulness and Mental Health
Dealing with a chronic condition can lead to feelings of anxiety or depression. Consider seeking therapy or counseling to help manage these emotions. Practicing mindfulness and tending to your mental health can significantly impact your journey.
When to Seek Medical Attention
While many people with adrenal insufficiency manage their symptoms well, there are times when you should reach out to your healthcare provider:
- Increased Symptoms: If you notice a sudden increase in fatigue, confusion, or other symptoms.
- Illness or Injury: During times of illness or injury, your body may require more medication.
- Missing Medication: If you accidentally miss a dose or experience gastrointestinal symptoms that prevent you from taking your medication.
Conclusion
Understanding adrenal insufficiency, or Addison’s disease, can bring clarity to what you or a loved one may be experiencing. By recognizing the symptoms, undergoing proper diagnosis, and adhering to treatment plans, you can manage the condition effectively and maintain a fulfilling life. Remember, you’re not alone in this journey, and there are resources and support out there to help you. Keep prioritizing your health, and don’t hesitate to reach out for support when needed.